Learning Notes - Azure Challenge
This blog is about the Azure developer challenge from Sparebanken Vest. I would like to write the learning notes here.
Explore Azure App Service
Target:
Learn about the key components of Azure App Service and how App Service can help you create, maintain, and deploy web apps more efficiently.
Azure App Service
So what is Azure App Service? It's a Http-based service, which would server for web application, REST APIs and mobile backends. It can:
- auto scale support
- CI/CD support
- Deployment slots -- support different deployment environment, like stage, prod
- Linux support. But have some limitaions:
- Not support on Shared pricing tier;
- Cannot mix Windows and Linux in same App service plan;
- Cannot mix Windows and Linux apps in the same resource group after Jan 21, 2021;
- Azure Portal shows only working features
Azure App Service plans
An app runs in an App Service plan and each plan defines:
- Region (West US, North Euro, etc)
- Number of VM instances
- Size of VM instances
- Pricing tier (Free, Shared, Basic, Premium and etc)
And pricing tier decides what feature you can use:
- Shared compute: Both Free and Shared share the resource pools and can't scale out.
- Dedicated compute: The Basic, Standard, Premium, PremiumV2, and PremiumV3 tiers run apps on dedicated Azure VMs.
- Isolated: This tier runs dedicated Azure VMs on dedicated Azure Virtual Networks and provides the maximum scale-out capabilities.
- Consumption: This tier is only available to function apps. It scales the functions dynamically depending on workload.
In the Free and Shared tiers, app cannot scale out. And apps in the same App Service plan would share the same VM instances.
When we add a new app, we need to understand the expected load for the new app. If it
- is resource intensive;
- needs resource in other geographical region;
- is scaled out independently from other apps; , we can isolate it into a new App Service plan.
Deploy
We can deploy App Service automatically from
- Azure DevOps
- Github
- Bitbucket
Or manually through:
- Git
- CLI -
az webapp upwould create a new App Service web app and deploy it; - Zip deploy - Use
curlor similar Http utility to send a ZIP to App Service; - FTP/S
Deployment slots can be used when deploying a new production build.
Authentication and Authorization in App Service
Built-in authentication can save time and effort with OpenID identity providers:
- Microsoft Identity Platform
- Any OpenID connect provider
The authentication and authorization will run in the same sandbox as application code and every incoming Http request would be handled with:
- authenticating with the specified provider
- validating, storing and refreshing tokens
- managing the authenticated session
- injecting identity information to request headers
Authentication flow:
- Sign user in
- Post authentication
- Establish authenticated session
- Serve authenticated content
In Azure portal, we can also configure App Service when the request is not authenticated:
- Allow unauthenticated requests
- Require authentication with Http 401/403
Networking features
Sometimes we need to control the inbound and outbound network traffic. And features of inbound and outbound cannot be used to each other.
| Inbound features | Outbound features |
|---|---|
| App-assigned address | Hybrid Connections |
| Access restrictions | Gateway-required virtual network integration |
| Service endpoints | Virtual network integration |
| Private endpoints |
But we can mix some features to solve the problems with a few exceptions.
| Inbound use case | Feature |
|---|---|
| Support IP-based SSL needs for your app | App-assigned address |
| Support unshared dedicated inbound address for your app | App-assigned address |
| Restrict access to your app from a set of well-defined addresses | Access restrictions |
Scale apps in Azure App Service
Target
Learn how autoscale operates in App Service and how to identify autoscale factors, enable autoscale, and how to create sound autoscale conditions.
Autoscale factors
Autoscaling can be triggered by defined rules and also deallocate resources when workload has diminished.
Azure provides two options for autoscaling:
- Scale based on a metric, like:
- CPU Percentage.
- Memory Percentage.
- Disk Queue Length.
- Http Queue Length.
- Data In.
- Data Out.
- Scale to a specific instance count according to a schedule. For example, you can arrange to scale out at a particular time of day, or on a specific date or day of the week. You also specify an end date, and the system will scale back in at this time.
Azure App Service deployment slots
Target
In this module you will learn how slot swapping operates and how to perform a swap. You will also learn how to route traffic to different slots manually and automatically.
Explore staging environments
Deployment slot is supported in the Standard, Premium, or Isolated App Service plan tier.
The benefits to have the non-production deployment slot is
- validate the app changes in the staging environment
- Deploy an app and swap with production deployment can eliminate the downtime
- Easy to swap back to the last good site if the swapped one is not as we expected
Develop for Azure Cache for Redis
Target
Learn how to configure Azure Cache for Redis, interact with the cache, and connect an application to Azure Cache for Redis by using .NET.
Scenarios
| Pattern | Description |
|---|---|
| Data cache | Databases are often too large to load directly into a cache. It's common to use the cache-aside pattern to load data into the cache only as needed. When the system makes changes to the data, the system can also update the cache, which is then distributed to other clients. |
| Content cache | For static content for template. We can use in-memory cache to provide quick access |
| Session store | Commonly used in shopping carts or user history data that might associate with cookie. But the data is too large for cookie. We can use Cookie as a key to query the data in in-memory cache, to associate information with a user quickly. |
| Job and message queuing | Applications often add tasks to a queue when the operations associated with the request take time to execute. Longer running operations are queued to be processed in sequence, often by another server. This method of deferring work is called task queuing. |
| Distributed transactions | Azure Cache for Redis supports executing a batch of commands as a single transaction. |
Configuration
Recommend always use Standard or Premium Tier for production system.
With Premium tier, you get supports:
- Virtual Network
- Clustering
The access key is like the password to cache. There are a primary and a secondary key, we can use either, but we should update the key periodically.
Implement Azure Key Vault
Target
Learn how Azure Key Vault can help you keep your apps more secure, and how to set and retrieve secrets by using the Azure CLI.
Explore Azure Key Vault
The Azure Key Vault service supports two types of containers: vaults and managed hardware security module(HSM) pools.
Azure Key vault would manage:
- Secrets - tokens, passwords, certificates, API keys, and other secrets
- Key - encryption keys used to encrypt your data.
- Certificate - public and private Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security (SSL/TLS) certificates
A Premium tier would include hardware security module(HSM)-protected keys.
Benefites:
- Centralized application secrets
- Securely store secrets and keys
- Monitor access and use
- Simplified administration of application secrets
Best Practices:
Use separate key vaults: Recommended to use a vault per application per environment (Development, Pre-Production and Production).
Control access to your vault: Key Vault data is sensitive and business critical, you need to secure access to your key vaults by allowing only authorized applications and users.
Backup: Create regular back ups of your vault on update/delete/create of objects within a Vault.
Logging: Be sure to turn on logging and alerts.
Recovery options: Turn on soft-delete and purge protection if you want to guard against force deletion of the secret.
Authenticate to Azure Key Vault
Authentication with Key Vault works in conjunction with Azure Active Directory, which is responsible for authenticating the identity of any given security principal.
Access tokens must be sent to the service using the HTTP Authorization header:
1PUT /keys/MYKEY?api-version=<api_version> HTTP/1.1
2Authorization: Bearer <access_token>
Explore Azure Cosmos DB
Target
Learn the core features and functionality of Azure Cosmos DB.
Benefits
- Unlimited elastic write and read scalability.
- 99.999% read and write availability all around the world.
- Guaranteed reads and writes served in less than 10 milliseconds at the 99th percentile.
Explore the resource hierarchy
hierarchy of different entities in an Azure Cosmos DB account
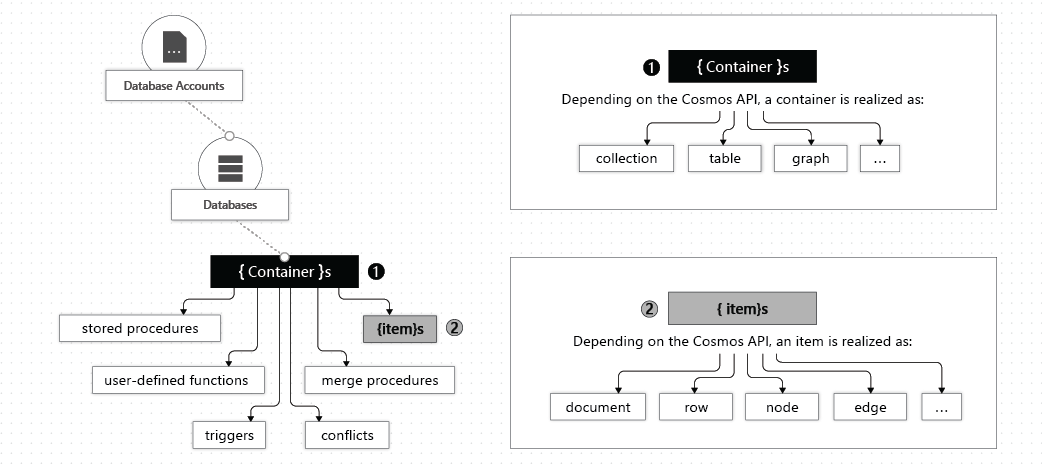
An Azure Cosmos database is mapped to various API-specific entities:
| Azure Cosmos entity | SQL API | Cassandra API | Azure Cosmos DB API for MongoDB | Gremlin API | Table API |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Azure Cosmos database | Database | Keyspace | Database | Database | N/A |
The mapping of API-specific entities to an Azure Cosmos item:
| Cosmos entity | SQL API | Cassandra API | Azure Cosmos DB API for MongoDB | Gremlin API | Table API |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Azure Cosmos item | Item | Row | Document | Node or edge | Item |
Consistency
With Azure Cosmos DB, developers can choose from five well-defined consistency models on the consistency spectrum. From strongest to more relaxed, the models include:
- strong
- bounded staleness
- session
- consistent prefix
- eventual
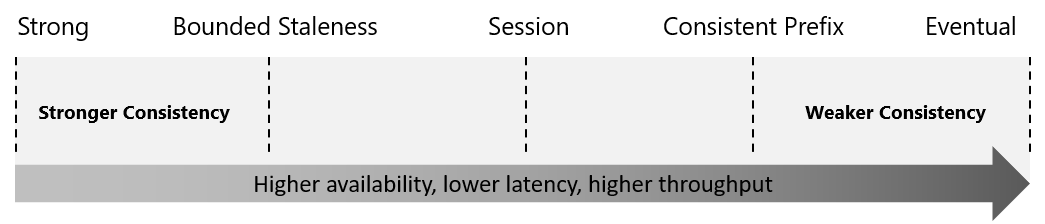
TBC
Explore the Microsoft identity platform
Target
Learn the core features and functionality of the Microsoft identity platform which includes authentication service, open-source libraries, and application management tools to enable and control access to resources.
Components
Microsoft identity platform consist of several components:
OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect standard-compliant authentication service enabling developers to authenticate several identity types, including:
- Work or school accounts, provisioned through Azure Active Directory
- Personal Microsoft account, like Skype, Xbox, and Outlook.com
- Social or local accounts, by using Azure Active Directory B2C
Open-source libraries: Microsoft Authentication Libraries (MSAL) and support for other standards-compliant libraries
Application management portal
Application configuration API and PowerShell
Service principals
An application must be registered with an Azure Active Directory tenant.
Create and deploy Azure Resource Manager templates
Target
Learn how Azure Resource Manager (ARM) can help streamline deployments, choose the correct deployment mode for your solution, and create and deploy an ARM template.
Microsoft Graph
Target
Learn how Microsoft Graph facilitates the access and flow of data and how to form queries through REST and code
Microsoft Graph is the gateway to data and intelligence in Microsoft 365. It provides a unified programmability model that you can use to access the tremendous amount of data in Microsoft 365, Windows 10, and Enterprise Mobility + Security.
Three main components to access and facilitate data:
- The Microsoft Graph API offers a single endpoint, https://graph.microsoft.com
- Microsoft Graph connectors
- Microsoft Graph Data Connect
Best practices
Consent and authorization:
- Use least privilege
- Use the correct permission type based on scenarios.
- Consider the end user and admin experience.
- Consider multi-tenant applications.
Handle responses effectively
- Pagination
- Evolvable enumerations
Provision virtual machines in Azure
Target
Learn the availability and sizing options of Azure Virtual Machines, and how to create a virtual machine by using the Azure CLI.
Explore Azure virtual machines
Design considerations for virtual machine creation:
- Availability
- VM size
- VM limits - The current limit on a per subscription basis is 20 VMs per region
- VM image
- VM disks
- Standard disks - HDDs, deal for a cost effective dev and test workload
- Premium disks - SSD, Perfect for VMs running production workload.